SAP Datasphere is SAP’s strategic target solution for all data warehouse and data management use cases in the public cloud. Due to its diverse functionalities around data integration, data cataloging, semantic modeling, data warehousing, data federation and data virtualization, SAP Datasphere is suitable for a wide range of scenarios. We present three selected use cases in which SAP Datasphere leverages its specific strengths.
How SAP BW customers move to SAP Datasphere
Scenario #1: Self-service BI
SAP Datasphere places a strong focus on self-service functionalities. The Business Builder establishes a business view on the objects of the data layer and is designed for semantic modeling. The goal behind this is to involve the business departments more strongly in data modeling in order to relieve IT and implement requirements more quickly.
For self-service BI to work, the data quality and the availability and performance of the system must be right. The task of providing the right framework for data modeling lies with the IT department. Among other things, the data must be harmonized and prepared. In addition, trained key users are needed in the specialist areas who have the necessary know-how to interpret the data correctly and create meaningful analyses. The key users act as a link between business and IT.
By providing separate modeling spaces for IT and business, SAP Datasphere enables a strict division between the departments. IT focuses on the core technical issues: It takes care of cleansing and preparing data from various sources, implements the general business logics, ensures high availability and performance of views and tables, and regulates data access control by managing permissions.
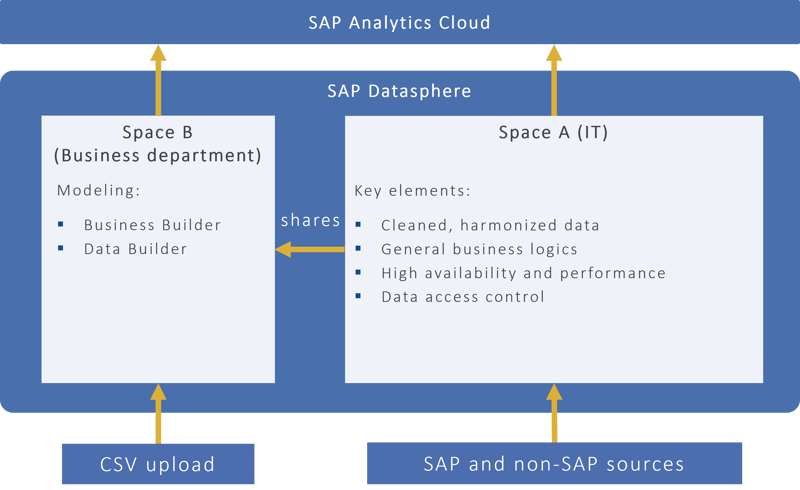
The Space concept of SAP Datasphere enables extensive self-service functionalities for the business department.
The IT space shares the objects with the spaces of the business departments so that the business departments can access the prepared content. This prevents data redundancies. The business units model with the Business Builder or with the Data Builder based on the prepared data models. They also have the option of enriching and supplementing the data models with CSV uploads.
Scenario #2: Hybrid modeling to extend an SAP BW solution
So far, a typical reporting architecture often looks like this: SAP BW/4HANA gets data from an ERP system like SAP S/4HANA – using a classic data flow with transaction and master data and implemented business logic. A future target picture could be that data modeling in SAP Datasphere takes place with data from the SAP BW system. The underlying data models should continue to be used in SAP Datasphere and the business units should be able to enrich the models using self-service functionalities. There are two options for implementing these requirements: the SAP BW/4HANA Model Transfer (if SAP BW/4HANA is in use) or the use of SAP BW Bridge.
SAP BW Bridge is an extension of SAP Datasphere with SAP BW functionality that makes it possible to migrate data flows from on-premise systems to the cloud. In a sense, it is a functionally reduced version of SAP BW/4HANA 2021. SAP BW Bridge does not provide an OLAP engine, which is why queries cannot be displayed or processed. The basis for SAP BW Bridge is the ABAP server (steampunk) available on SAP HANA Cloud. Thanks to it, ABAP functionalities can also be used, while SAP Datasphere is SQL-based. SAP BW Bridge models are deployed in SAP Datasphere via a special space. The data models can be imported either as remote tables or via model transfer.
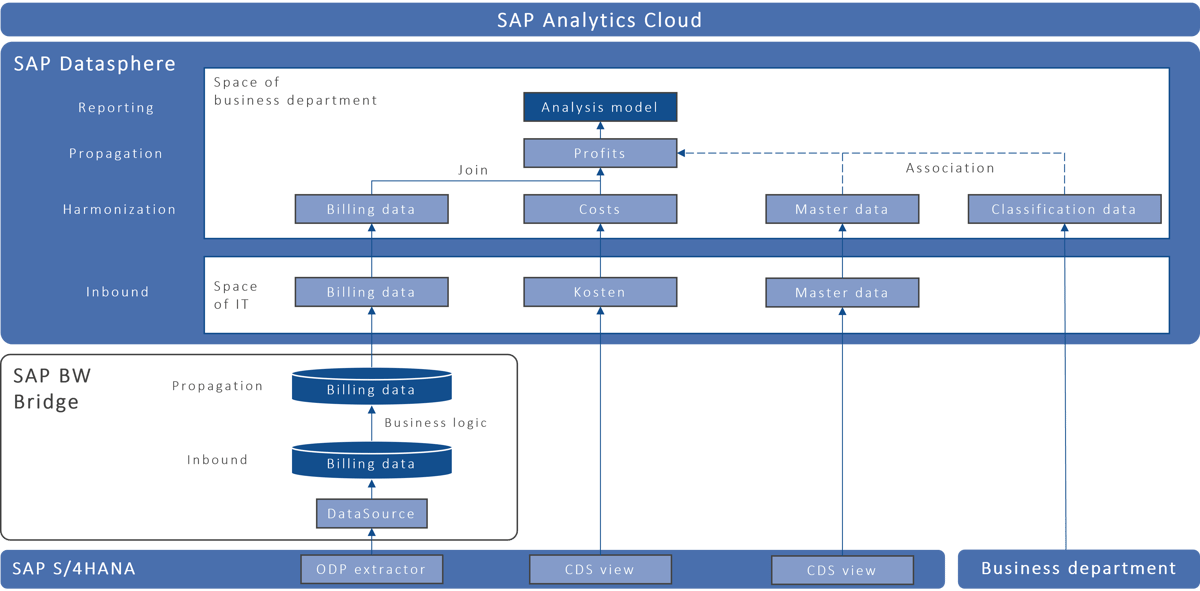
Using SAP BW Bridge or SAP BW/4HANA Model Transfer, data modeling in SAP Datasphere can take place with data from the SAP BW system.
In an existing SAP BW 7.5 or SAP BW/4HANA landscape, there are two ways to migrate the data flows into SAP BW Bridge. While only the metadata is transferred during shell conversion, metadata, object definitions and data are transferred during remote conversion. SAP BW 7.x objects are loaded into SAP BW Bridge and converted into SAP BW/4HANA objects.
The SAP BW/4HANA Model Transfer offers the possibility to bring data models based on analytical queries to SAP Datasphere. Metadata and data can be transferred without manual re-creation. Required objects such as views or tables are automatically generated in the Data Builder or the Business Builder of SAP Datasphere. The SAP BW/4HANA Model Transfer does not work with older releases such as SAP BW 7.5. For these systems, there is an option to use SAP BW as a data source via SDI/SDA in SAP Datasphere.
The general recommendation is that if an SAP BW/4HANA system is available, the data should be federated via SAP BW/4HANA Model Transfer to import the queries. The use of SAP BW Bridge is always recommended if complete data flows are to be transferred or SAP S/4HANA extractors are to be connected or if performance problems occur during data federation.
Scenario #3: Real-time reporting with SAP S/4HANA
In real-time reporting, data is drawn directly from SAP S/4HANA, processed in real-time in SAP Datasphere, and output in reporting. In this case, real-time means that the data is updated promptly – within minutes or hours. The prerequisite for real-time reporting is that the data is loaded via real-time replication. To keep query intensity low, only critical data such as product and customer master data and transaction data should be replicated in real time so that real-time replication does not negatively impact performance. The data is extracted from SAP S/4HANA via CDS views. Change Data Capture (CDC) enables delta-enabled loading of CDS views. This way, only the data that has been changed is updated.
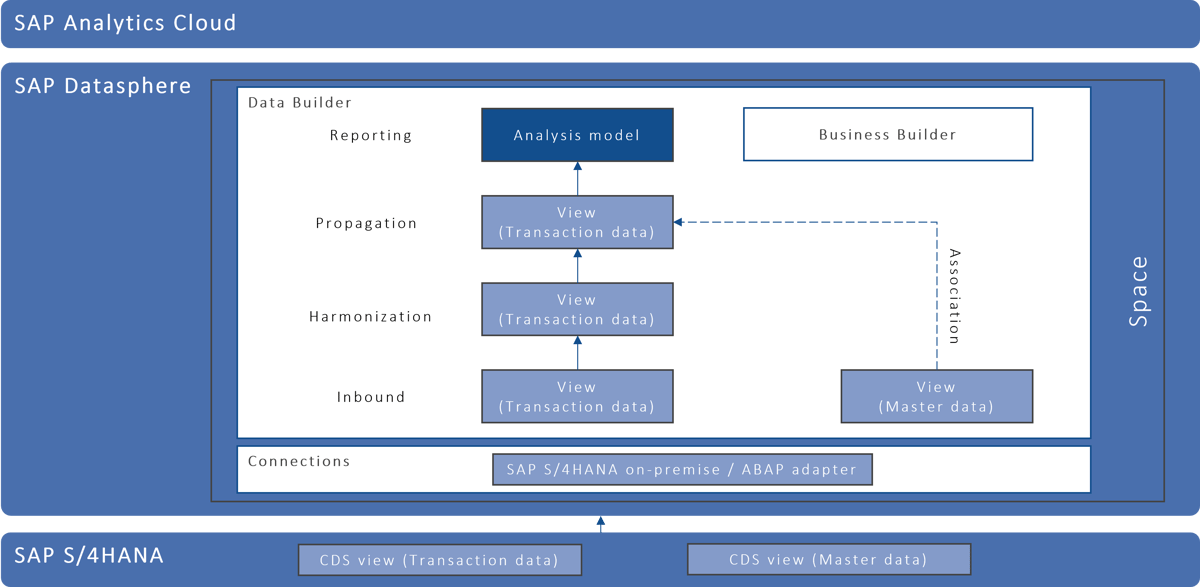
SAP Datasphere enables real-time reporting with SAP S/4HANA.
The approach of using CDS views for extraction instead of accessing tables directly proves to be significantly more performant. The frequency of queries should be reduced using snapshots. Depending on requirements, snapshots can be scheduled on a daily or weekly basis, for example.
Conclusion: SAP Datasphere promotes business success
From self-services to hybrid data modeling to real-time reporting, SAP Datasphere’s diverse functionalities and deployment options contribute directly to business success. Advanced self-service capabilities enable business users to access and analyze the data they need without relying on IT. This accelerates decision-making and improves business performance. Real-time reporting ensures that the most up-to-date data is always available. This empowers businesses to make informed decisions and take proactive actions to address existing challenges or take advantage of emerging opportunities.
![IBacademy_Logo_blau[496] IBacademy_Logo_blau[496]](https://www.ibsolution.com/hs-fs/hubfs/IBacademy_Logo_blau%5B496%5D.jpg?width=200&name=IBacademy_Logo_blau%5B496%5D.jpg)







