As a component of SAP Financial Supply Chain Management (FSCM), SAP Dispute Management is used to process receivables-related dispute cases. If a business partner arbitrarily reduces agreed payments, companies must follow up and clarify the case. Possible reasons for the reduced amount could be damaged goods or outdated prices that were mistakenly still stored in the system. Without the right software support, such follow-ups are time-consuming and involve long processing times, since several employees from different departments have to coordinate their efforts and also have to exchange information with the customer. This means that the capacities of the employees dealing with the dispute case are not available for other tasks.
SAP Dispute Management is part of SAP Financial Supply Chain Management
Structuring dispute cases and documenting processes
For such scenarios, SAP Dispute Management offers an efficient solution approach by creating, structuring and coordinating dispute cases in the SAP S/4HANA system. Each dispute case is assigned its own case ID, and all transactions and all relevant information for dispute case processing are documented under this case ID so that they can still be traced at a later date. With SAP Dispute Management, the accounts receivable department has an overview at all times of which dispute cases are still open, what the respective status of the dispute is, and what outstanding amounts are involved. Integration with the SAP S/4HANA application SAP FI (Financial Accounting) ensures that the open item is cleared directly and the dispute case is automatically set to “Closed” as soon as the outstanding payment is received.
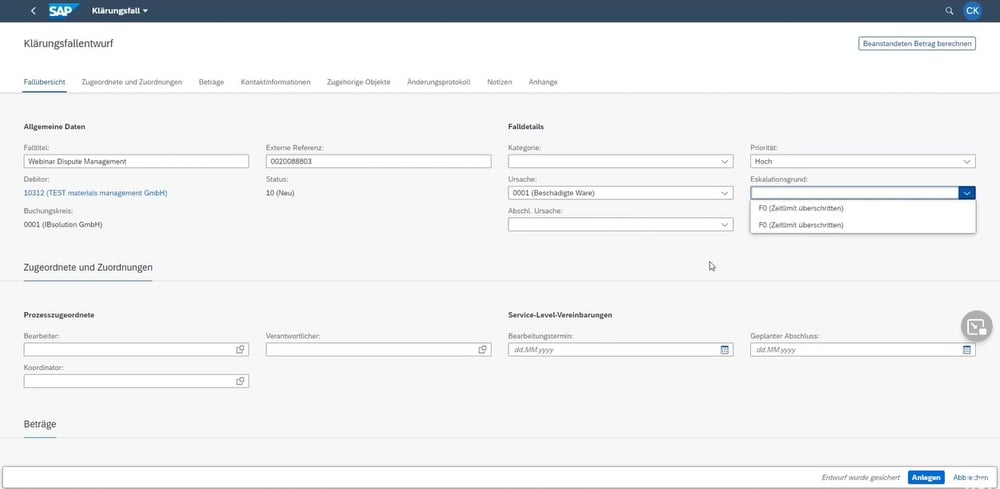
SAP Dispute Management makes it quick and easy to create dispute cases.
Process flow and responsibilities for a dispute case
Typically, the process for a dispute case is as follows: An open item arises because a customer owes the company money for a product or service. When payment is received, an underpayment is identified and a residual item is created for the outstanding amount. SAP Dispute Management now creates a dispute case because there is a difference between the original receivable and the settled amount. The dispute case can be closed either by a settlement payment from the customer or by a credit memo, so that the residual item is settled.
When creating the dispute case, SAP Dispute Management offers the possibility to define a processor, a responsible person and a coordinator. The processor is responsible for coordinating and documenting the dispute case and the further procedure with the customer. This task can be performed, for example, by a sales employee who is in contact with the customer anyway.
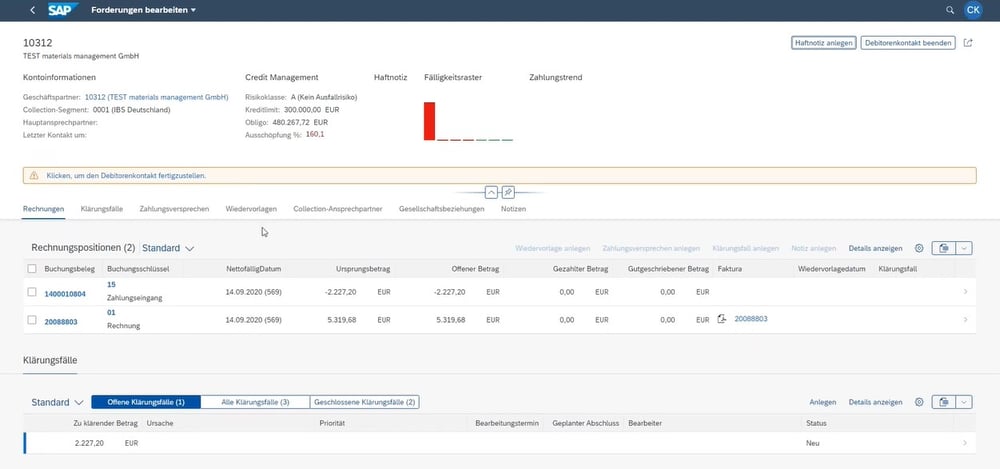
Thanks to integration with SAP FI, detailed information on debtors can be retrieved.
The person responsible, such as an accounts receivable accountant, creates the dispute case and regularly checks the dispute cases assigned to him or her via line item display. The coordinator – who may be the head of accounts receivable – monitors all dispute cases and has the option of using Fiori apps to perform structured evaluations and use various graphical display options for this purpose. For example, he can visualize how many clarification cases have been processed in a certain period of time and the total volume of the currently open clarification cases.
Conclusion: Efficient and fast processing of dispute cases
SAP Dispute Management enables greater efficiency and shorter processing times when handling dispute cases. All relevant information is available in one system without media breaks. Integration with SAP FI means that dispute cases are automatically closed when clearing entries are received.
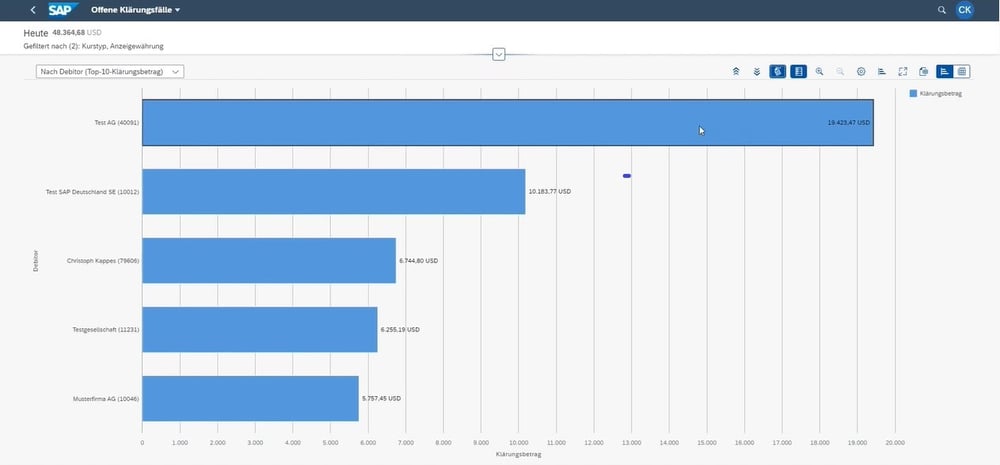
The numerous evaluation options via Fiori apps enable meaningful reporting.
The analytical Fiori apps clearly prepare all relevant information relating to a company’s dispute cases. Various control parameters can be flexibly selected, for example, to display the dispute cases by processor or status. In addition, business partners who frequently fail to meet their payment obligations can be identified. In this way, SAP Dispute Management creates a suitable basis for seeking targeted discussions with these business partners.
![IBacademy_Logo_blau[496] IBacademy_Logo_blau[496]](https://www.ibsolution.com/hs-fs/hubfs/IBacademy_Logo_blau%5B496%5D.jpg?width=200&name=IBacademy_Logo_blau%5B496%5D.jpg)







