The forecast is becoming increasingly important as a management tool for companies, especially in times of dynamic change. With a forecast concept tailored to the company’s requirements, target achievement can be regularly monitored. In the event of deviations from the plan, effective countermeasures can be taken to get business development back on track.
The faster the general conditions change, the more the forecast must be able to take these changes into account. High market dynamics, for example, increase the need for simulations in the forecast. The forecast horizon becomes shorter, while the frequency of the forecast increases. As complexity increases, so does the need to embed the forecast in a powerful IT environment.
Clear distinction between planning and forecasting (a forecast is not a new planning)
Starting point: Definition of forecast goals (What should be achieved with the forecast?)
Determination of the appropriate forecast approach (trend, effects, predictive, etc.) based on the business environment
Reduction of manual inputs to a minimum to eliminate sources of error
Focusing on the parameters relevant to control
Differentiated detailing depending on function or business area
Minimization of the lead time of the forecast process to a maximum of three weeks
Shortening of coordination rounds and avoidance of idle times through uniform data basis, common templates as well as consistency and plausibility checks
Use of an electronic workflow
Default values as starting point for the forecast
Connection of operational data, for example from supply chain management
Identical, coordinated and consistency-checked output data for all participants
Acceptance of “bad news” (deviations from target achievement)
Tracking of forecast data in actual reporting including analysis of reasons for deviations
Measurement of forecast quality with deviation “actual to forecast” as quality measure and, if necessary, incentivization
Establishment of a management dialog with regard to the presented forecast
Discussion of the steering impulses to be derived from the forecast (for example, reallocation, increase or reduction of budgets)
Facilitation of the dialog with management by linking measures and business-specific driver models
Definition of operational measures to achieve targets
Quarterly consideration of strategic measures in the forecast
Creation of transparency about the contribution of different measures to the achievement of objectives
Individual adaptation of the forecast concept to the respective company
Consideration of the dynamics and complexity of the business environment when selecting the concept
The performance of the IT environment and the corporate culture also play a role

“The part of forecasting and financial agility most urgently in need of improvement is speed. (…) This urgency has come about because organizations can’t plan or execute strategic initiatives without the insight that planning, budgeting and forecasting provides. But the external environment has been changing so rapidly over the last (…) years that the parameters need to be adjusted frequently. Without it, organizations will be depending on out-of-date intelligence and lose any competitive advantage they may have had.”
Source: FSN Global Survey “Future of Planning, Budgeting, Forecasting and Reporting”, August 2022
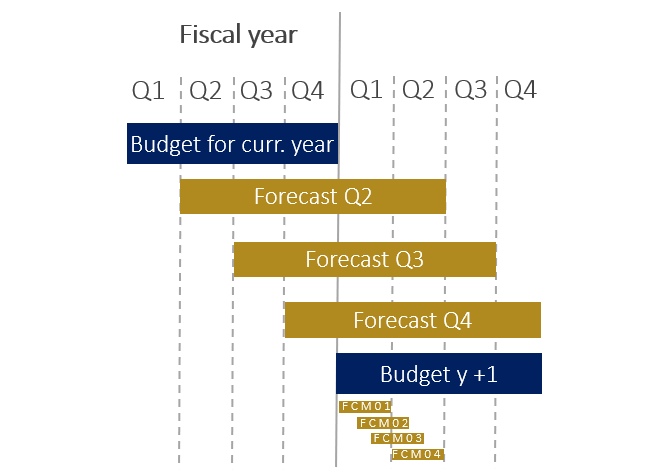
With the rolling forecast, the planning horizon always remains constant, for example by planning the next four quarters on a quarterly basis. This is pure “forward control”.
The forecast is updated on the basis of new projections of the financial control parameters across the levels. The focus is on the aspects of early warning and flexibility.
The rolling forecast is an important management tool, especially for companies operating in dynamic market environments. In more static environments, the approach is of less benefit, as limited new insights are offset by significant effort.
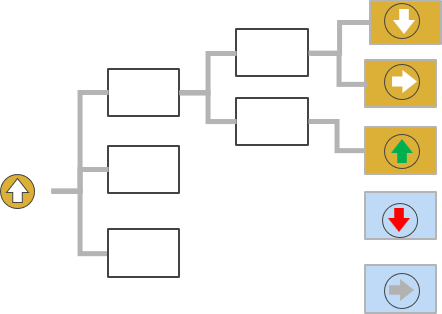
The focus of the driver-based forecast is on clearly defined, business-specific cause-and-effect relationships. The forecast is updated by projections on the development of the main operating drivers. The driver-based forecast provides an excellent starting point for simulations and measure-oriented management.
A prerequisite for the high effectiveness of the driver-based forecast is a clear understanding of the business model including the cause-effect relationships and the operational drivers. A key strength lies in the focus on the essential control parameters. There is no detailed, cost center-specific planning of all cost items. Due to the complexity, the mapping of different business/driver models requires powerful IT support.
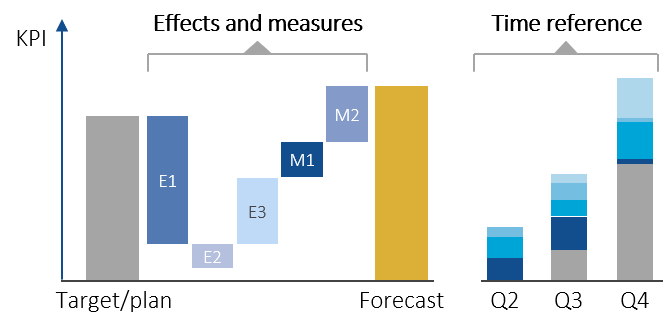
The basic approach of the effects-based forecast is that the budget is initially also confirmed as the target during the year and only significant individual effects and measures are taken into account in the forecast. The budget values, not the actual values, serve as the starting point for the past months. Unlike other forecasting concepts, effects and measures are not determined on the basis of modeled calculation methods, but are the result of estimates and discussions at management level.
The effects-based forecast is very efficient because it focuses on significant, known effects. In addition, the results have a high degree of transparency regarding deviations and measures.
An important feature of this approach is the promotion of a culture of target achievement instead of the widespread sign-off of budget targets. The classic approach – to the actual, which can no longer be changed, a “to go” is planned that is as realistic as possible – is virtually reversed.
The effects-based forecast is particularly suitable for high-level considerations. It is therefore perfectly possible to use the effects-based forecast as a complement to conventional forecasting concepts, for example at group level.
In our series of workshops on forecasting, we work with you to examine the current situation with a view to existing control elements. In addition, the guidelines for your future forecast concept will be adopted and documented. Relevant aspects include granularity, data origin, data availability and quality, and responsibilities. We also analyze which process-related prerequisites must be created for the forecast in your company.
In highly dynamic and very complex business environments, the effectiveness of modern forecasting concepts such as effects-based, driver-based or rolling forecasts can reach their limits. Such settings therefore require differentiated approaches that are strongly data-driven and rely on powerful IT support.
Innovative technologies such as machine learning and artificial intelligence enable self-learning algorithms that recognize correlations and dependencies from the data and in this way significantly increase the quality of the forecast (Predictive Analytics). At the same time, the forecast horizon is reduced to a few weeks or even days. The values generated by the system are suggestions. Manual adjustment is still possible.
The supreme discipline in forecasting is Prescriptive Analytics. Here, the data-driven forecast is extended to include automatic suggestions for action. The result is a high level of objective forecast quality and data-supported decisions that make a significant contribution to operational excellence.
Business-specific, accepted driver models
Resilient, available data basis
Modern IT systems (speed, functionalities)
Acceptance of short-term control
Basic understanding of/for statistics and modeling
Mix of predictive models, pre-systems, etc.
Simply complete the form and submit it. We will contact you as soon as possible.
Benefit from our know-how




Precise, reliable business planning is a crucial success factor, especially in times of dynamic and complex market situations. To modernize and optimize your business planning, we have identified twelve decisive levers that reduce the effort required for planning or increase its benefits.

The challenges that companies are facing in current times are enormous. The high dynamics of change make it necessary for companies to adapt their processes to the new framework conditions.
