The switch to SAP S/4HANA requires the implementation of SAP Credit Management. The classic credit management module FI-AR-CR no longer exists under SAP S/4HANA. The main purpose of SAP Credit Management is to identify default risks at an early stage and mitigate financial losses. The solution calculates the creditworthiness of business partners, taking past payment behavior into account. Alternatively, external credit agencies can be integrated for the calculation of creditworthiness. SAP Credit Management makes it possible to achieve greater efficiency in credit decisions and processes. Manual activities are reduced to a minimum.
We support you on the way to new SAP Credit Management
Functionalities in the new credit management
The differences between the previous credit management FI-AR-CR and SAP Credit Management are considerable. Although the credit control areas from FI-AR-CR remain, credit segments are introduced in addition. They form the organizational unit of SAP Credit Management. It is possible to combine several credit control areas into one credit segment.
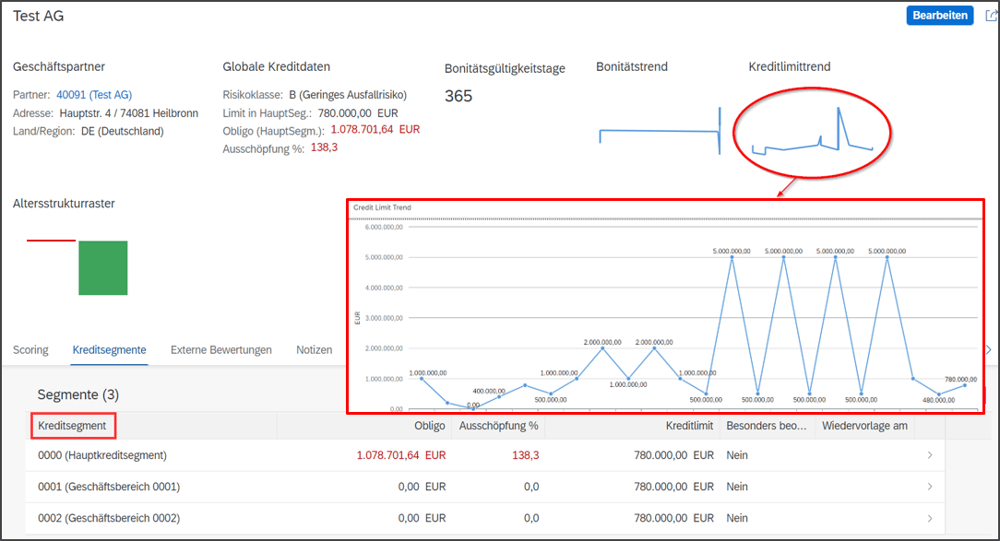
SAP Credit Management also harmonizes master data: creditworthiness, risk class, credit group and credit check are managed centrally across all credit segments. Corresponding parameters are stored for each business partner and are no longer determined separately for each credit control area. Higher-level credit accounts and credit officers can be maintained in the Business Partner master data record in the “Business Partner Relationships” tab.
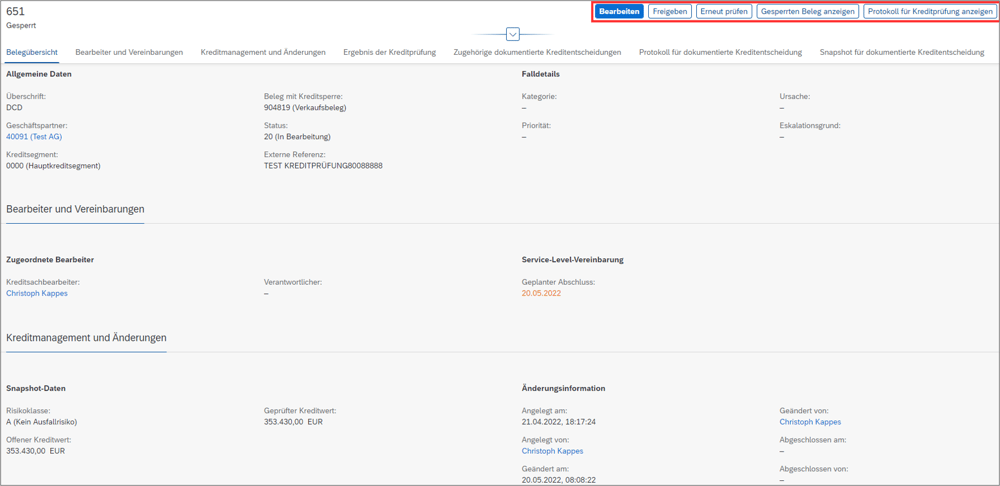
Case Management is a component of SAP Credit Management that allows users to process workflows and manage and document credit limit requests and blocked documents. In classic credit management, the VKM1 transaction was available for this purpose. Once a credit limit request has been released in Case Management, the credit limit is automatically increased in the Business Partner.
Additional license for SAP Advanced Credit Management
In its basic version, SAP Credit Management is included in the SAP S/4HANA standard. SAP Advanced Credit Management, on the other hand, requires an additional license. Compared to SAP Credit Management, additional functionalities are available, such as the automatic calculation of internal creditworthiness, the derivation of the risk class from the internal creditworthiness, the calculation of credit limits and the storage of external credit reports. It is also possible to import creditworthiness, credit risk class and credit limits from external systems. Working with credit limit applications is also part of the scope of services. SAP Advanced Credit Management is suitable for setting up central credit management in a multi-system landscape.
Recommendation: independent pre-project
Even in its basic version, SAP Credit Management is a powerful module and exhibits a high level of complexity in terms of functions and processes. For this reason, it is advisable to implement SAP Credit Management as an independent pre-project before proceeding with the actual SAP S/4HANA migration. An important prerequisite for success is a detailed concept that describes exactly how SAP Credit Management is to be set up. Validation is required so that migration data, processes and external information can be imported. A cut-over plan can be used to record which tasks need to be completed before, during and after the migration. There are many new transactions in SAP Credit Management in SAP S/4HANA. Accordingly, the jobs and reports that are necessary in new SAP Credit Management to keep the data up-to-date must be scheduled and executed.
Important questions to ask before implementing SAP Credit Management
To best prepare for the introduction of the new credit management, companies should clarify a number of questions in advance. With regard to organizational units, for example, it is important to determine which credit control areas should continue to be used and which credit segments should be introduced. It is also relevant which credit segments are assigned to which credit control areas and which company codes are used for SAP Credit Management. In addition, the question arises as to which sales areas participate in SAP Credit Management.
As far as master data in SAP Business Partner is concerned, companies need to define the authorizations of sales and credit officers with regard to the maintenance of credit data. This includes deciding who (sales, credit officers, master data officers) is allowed to create the corresponding master data and what the exact procedure (approval workflow, dual control principle) should be. In addition, the question is relevant in which system the master data should be maintained: in SAP S/4HANA or, for example, in a master data tool such as SAP MDG, if it is available in the company.
Processing credit limit requests
With regard to credit limit requests, it must be determined who may request an increase or reduction in the credit limit and who makes the decision on whether to approve credit limit requests. Internal creditworthiness calculations, an internal rating or external credit agencies such as Creditreform or BaFin (Federal Financial Supervisory Authority) can be used as the basis for decision-making when determining credit limits.
For credit checks in SD documents, a decision is required as to which SD documents (offer, order, delivery) and which parameters (for example, credit limit, dunning level, order, delivery) are to be checked. Another question relates to what happens in the event of a negative credit check: Does the system simply issue an error or warning message, or does a document block occur? For the definition of risk classes, for example, a distinction between low, medium and high default risk is a good idea.
With regard to the documented credit decision (DCD) for releasing documents, it is necessary to define rules for dealing with blocked documents. Here, too, the first question is who is authorized to process documented credit decisions. In order to decide on blocked documents, internal creditworthiness, external credit agencies and previous business relationships can be used as a basis for decision-making. Furthermore, it must be defined which fields in the processing screen of blocked documents are relevant and should therefore be defined as mandatory fields, for example.
Check creditworthiness
The automated creditworthiness calculation is used to identify default risks for new customers at an early stage. The basis for this is the creditworthiness check. It can be carried out as an upstream process during the offer initiation process. Automatic calculation of creditworthiness and credit limit is possible at any time.
In addition, the automated creditworthiness calculation contributes to the optimization of business relationships. By acting proactively, payment terms can be adjusted or credit collateral can be requested, for example. The advantages of automated creditworthiness calculation are the reduction of financial defaults and the increase of efficiency in processes through automation without media discontinuity. Parameters for determining creditworthiness can include, for example, payment history (dunning levels, overdue items), the legal form of the company, the country from which the company originates, or information from external credit agencies. Basically, it must be determined how the parameters are weighted and which risk classes are to be assigned at which creditworthiness value. Possible knock-out criteria are insolvency proceedings, declarations in lieu of an oath or foreclosures.
Conclusion: Develop awareness of the changes
Compared to the classic credit management module FI-AR-CR, the new SAP Credit Management brings with it various fundamental innovations in terms of functionalities and logic. The most important ones are the Business Partner as a master data object, new transactions and reports that are available, and Case Management. It is important that companies develop an understanding of the innovations and are aware of the far-reaching effects that come with SAP Credit Management. Ideally, companies implement SAP Credit Management in an independent pre-project. It is recommended that a detailed functional concept be drawn up, which should not least clarify the authorizations of sales and credit managers.
![IBacademy_Logo_blau[496] IBacademy_Logo_blau[496]](https://www.ibsolution.com/hs-fs/hubfs/IBacademy_Logo_blau%5B496%5D.jpg?width=200&name=IBacademy_Logo_blau%5B496%5D.jpg)







