The understanding that high data quality is an elementary prerequisite for business success has now become established in almost all companies. Nevertheless, many companies fail in practice to maintain the quality of their data at a high level over the long term. In search of the causes, it turns out that a suitable organizational framework with processes, roles and responsibilities for transparent and reliable data management is often lacking − a framework that data governance can provide.
Defined responsibilities
Clearly divided data ownerships
Neatly defined and documented processes
Improved security
Fulfillment of compliance guidelines and legal requirements
Established data stewards
Data governance provides the organizational framework for consistent, disciplined data maintenance and high data quality. The white paper “Data Governance – How to create the basis for permanently high data quality in your company” describes why clear responsibilities and unambiguous roles are decisive prerequisites for ensuring high-quality data. Using concrete practical examples, it becomes clear how data governance promotes corporate success.
Create transparency and trust in data
Ensure reliability of data
Ensure data security and privacy
Ensure data availability and accessibility
Optimize data management
Lack of management commitment
Unclear responsibilities and accountabilities
High complexity of the data landscape
Unclear scope
Accompanying change management and acceptance
Data is increasingly becoming a decisive competitive factor. Mid-sized companies that manage and use their data effectively are able to make informed decisions and operate more successfully in the business world than their competitors. With a functioning data governance, they ensure that they access high-quality data and improve their decision-making.
Clear roles and responsibilities for data maintenance, access, and quality help mid-sized companies make their processes more efficient. In addition, data governance ensures that applicable compliance requirements are implemented and legal requirements regarding data protection are met.
In order for companies to make their data a long-term success factor, they must maintain their data quality at a permanently high level or increase it continuously. An effective data governance plays a decisive role in achieving this goal.
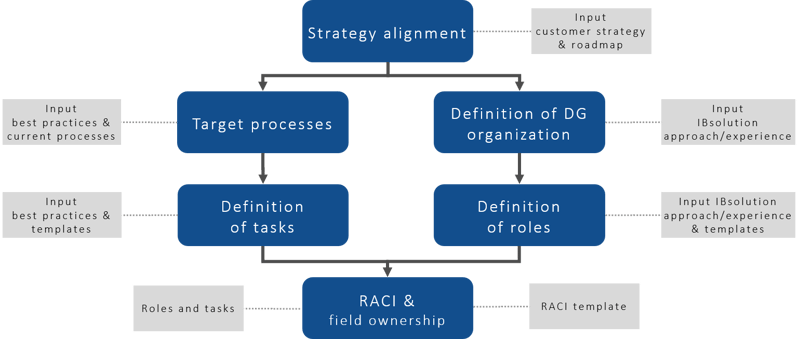
We address all relevant topics related to data governance in a pragmatic top-down approach (see below):
Based on the strategies, challenges and goals of the company, we analyze the existing processes and define an organizational model with corresponding roles.
Based on this, we define the responsibilities in a RACI matrix (RACI = Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, Informed) and assign detailed field responsibilities for all relevant data objects.
In a final step, we take care of the handover for implementation, plan the governance roll-out and install the new organization.
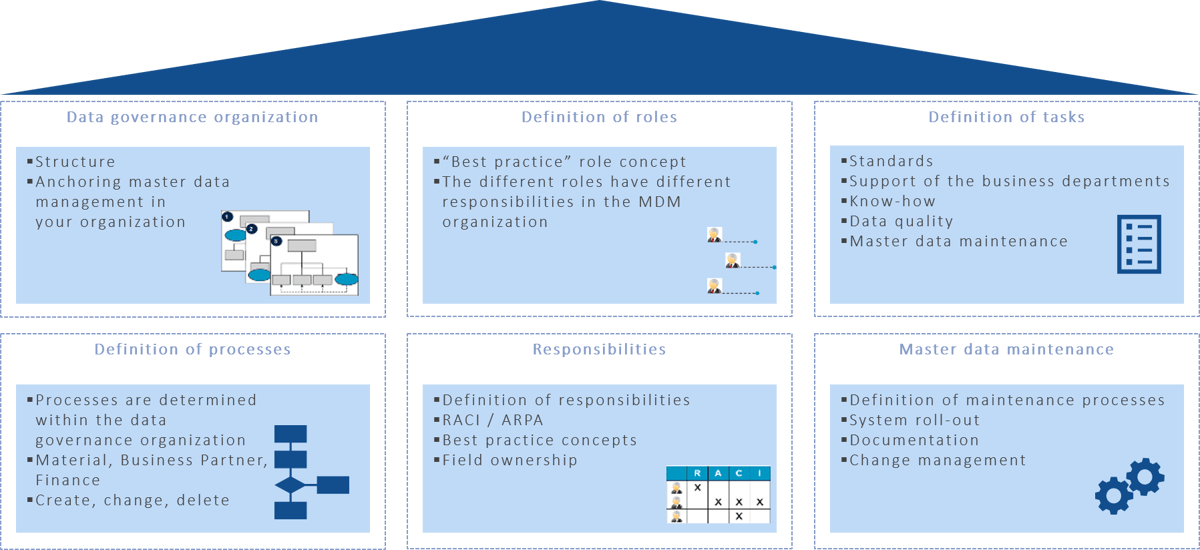 Based on our many years of experience in data management, we have developed a data governance framework with six pillars that creates the strategic framework for successfully managing data and permanently ensuring high data quality. This includes setting up a data governance organization and integrating it within the corporate structure. The definition of roles serves to clarify responsibilities and to create a sustainable role concept for the organisation. The tasks and activities that have to be performed within the framework of data governance are determined in the definition of tasks. This not only determines what needs to be done, but also which departments of the company perform the tasks.
Based on our many years of experience in data management, we have developed a data governance framework with six pillars that creates the strategic framework for successfully managing data and permanently ensuring high data quality. This includes setting up a data governance organization and integrating it within the corporate structure. The definition of roles serves to clarify responsibilities and to create a sustainable role concept for the organisation. The tasks and activities that have to be performed within the framework of data governance are determined in the definition of tasks. This not only determines what needs to be done, but also which departments of the company perform the tasks.
The definition of processes aims to describe, document and optimize the existing data processes. Assigning responsibilities creates a clear allocation of the role concept on the one hand to the tasks and processes on the other hand. The responsibilities are detailed with the help of a RACI matrix. In this context, the definition of ownership for the various data objects is also part of the process. Data maintenance defines how the theoretical descriptions are to be transferred to operational data management. The aim is not only to define the data maintenance processes from a functional point of view, but also to clarify the technical implementation and describe the change management.
 Although a standardized approach to data governance has proven itself, the individual characteristics of each company must be taken into account in every project. Data governance only has a chance of success if it is in line with the corporate strategy and supports it in the best possible way.
Although a standardized approach to data governance has proven itself, the individual characteristics of each company must be taken into account in every project. Data governance only has a chance of success if it is in line with the corporate strategy and supports it in the best possible way.
An analysis of existing processes provides information about how data management is currently organized in the company. Based on existing processes, an optimized set of processes is developed in line with industry standards and best practices. In parallel, the data governance organization within the corporate structure must be defined. Among other things, this involves the question of whether activities should be mapped centrally or organized in local units.
The next step is to derive tasks from the target processes and a role concept from the data governance organization. A RACI matrix links tasks and roles. In addition, the field ownerships are defined: Who has tactical responsibility for the fields? Who is responsible for operational data maintenance?
Once this theoretical framework is established, the roll-out into the organization takes place.






Support in deriving the data strategy from the corporate strategy
Support in the definition of measurable goals and the creation of a data roadmap
Joint development of a communication and change management strategy
Review and, if necessary, documentation of existing processes in the data environment
Support in the development of optimized target processes and tasks
Definition of the tasks in RACI
Documentation of the final framework, based on customer standards
Preparation of ownership templates and task definition
Coordination and moderation during the development of the ownership mapping
Support for the introduction of a data dictionary
Visualization of data maintenance processes (creation, modification, enhancement, blocking, deletion, ...)
Definition of the working model for process governance
Process documentation and training of process participants
Support in setting up data quality KPIs and a monitoring system
Setting up the data management organization
Supporting the coordinated roll-out with the SAP S/4HANA migration




A stable strategic foundation can provide the best possible support for the challenge of operational data management and maintenance. This foundation for data management in the company is called data governance.

Data governance encompasses people, processes, and technologies required to manage and protect data assets. In this webinar, we will show you how to set up data governance in your company.
Whatever it may be: simply complete the form and submit it. We will get back to you as soon as possible.